【实战】使用非root用户启动Rsyslog服务的两种方法

【实战】使用非root用户启动Rsyslog服务的两种方法
1 使用systemctl模式启动ryslog服务[非root用户]
1.1 允许非root用户使用1024以下端口
linux允许非root用户默认只能使用1024以上端口,sysctl 可以修改该起始端口。
例:允许非root用户使用所有端口
1 | |
1.2 编辑rsyslog服务端rsyslog.conf配置文件,添加启动用户配置参数
可以利用$PrivDropToUser、$PrivDropToUserID、$PrivDropToGroup和$PrivDropToGroupID配置指令以非root用户身份运行rsyslog。
使用这些变量时,rsyslog将以root身份启动,但在初始化完成后将下降到指定的用户或组。
然后,守护程序将根据指定用户或组的权限运行。
1 | |
编辑/etc/rsyslog.conf配置文件添加以下配置
1 | |
1.3 修改systemctl rsyslog服务启动用户
在 CentOS/RHEL 7 中,rsyslog 默认以 root 身份运行,以非 root 用户身份运行时会出现权限问题。
要确保您可以从/run/logs/journal中的systemd日志中获取日志记录,请将指定的用户修改为"systemd-journald"组的成员:
1 | |
1.4 使用rsyslog用户重启rsyslog服务
1 | |
1.5 修改/var目录下的log文件权限
让rsyslog用户有写的权限。
1 | |
1.6 修改/var/lib/rsyslog目录权限
这一步很重要
含义:让rsyslog用户能读取imjournal.state文件。
1 | |
1.7 验证日志接收
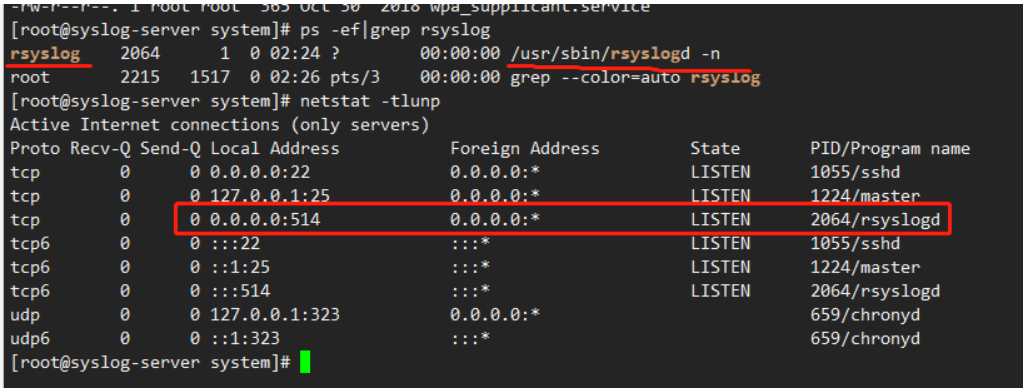
日志文件存在:

1.8 注意点
将rsyslog tls 密钥文件保存到/home/rsyslog目录中,或者让rsyslog用户有读取密钥文件的权限。
rsyslog数据保存路径,rsyslog用户需要有写的权限。
1.9 参考配置文件
1 | |
2 使用command模式启动rsyslog服务[非root用户]
2.1 创建rsyslog用户
创建rsyslog用户,并设置密码,必须步骤
1 | |
2.2 将rsyslog.conf和rsyslog TLS证书保存到rsyslog家目录中
将rsyslog.conf、rsyslog TLS证书全部保存到/home/rsyslog目录中
rsyslogd.conf 配置文件内容如下
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119# rsyslog configuration file
# For more information see /usr/share/doc/rsyslog-*/rsyslog_conf.html
# If you experience problems, see http://www.rsyslog.com/doc/troubleshoot.html
#### MODULES ####
# The imjournal module bellow is now used as a message source instead of imuxsock.
$ModLoad imuxsock # provides support for local system logging (e.g. via logger command)
$ModLoad imjournal # provides access to the systemd journal
#$ModLoad imklog # reads kernel messages (the same are read from journald)
#$ModLoad immark # provides --MARK-- message capability
# Provides UDP syslog reception
# $ModLoad imudp
# $UDPServerRun 514
# Provides TCP syslog reception
#$ModLoad imtcp
#$InputTCPServerRun 514
#### GLOBAL DIRECTIVES ####
# Where to place auxiliary files
$WorkDirectory /var/lib/rsyslog
# Use default timestamp format
$ActionFileDefaultTemplate RSYSLOG_TraditionalFileFormat
# File syncing capability is disabled by default. This feature is usually not required,
# not useful and an extreme performance hit
#$ActionFileEnableSync on
# Include all config files in /etc/rsyslog.d/
$IncludeConfig /etc/rsyslog.d/*.conf
# Turn off message reception via local log socket;
# local messages are retrieved through imjournal now.
$OmitLocalLogging on
# File to store the position in the journal
$IMJournalStateFile imjournal.state
#### RULES ####
# Log all kernel messages to the console.
# Logging much else clutters up the screen.
#kern.* /dev/console
# Log anything (except mail) of level info or higher.
# Don't log private authentication messages!
# *.info;mail.none;authpriv.none;cron.none /var/log/messages
# The authpriv file has restricted access.
authpriv.* /var/log/secure
# Log all the mail messages in one place.
mail.* -/var/log/maillog
# Log cron stuff
cron.* /var/log/cron
# Everybody gets emergency messages
*.emerg :omusrmsg:*
# Save news errors of level crit and higher in a special file.
uucp,news.crit /var/log/spooler
# Save boot messages also to boot.log
local7.* /var/log/boot.log
# ### begin forwarding rule ###
# The statement between the begin ... end define a SINGLE forwarding
# rule. They belong together, do NOT split them. If you create multiple
# forwarding rules, duplicate the whole block!
# Remote Logging (we use TCP for reliable delivery)
#
# An on-disk queue is created for this action. If the remote host is
# down, messages are spooled to disk and sent when it is up again.
#$ActionQueueFileName fwdRule1 # unique name prefix for spool files
#$ActionQueueMaxDiskSpace 1g # 1gb space limit (use as much as possible)
#$ActionQueueSaveOnShutdown on # save messages to disk on shutdown
#$ActionQueueType LinkedList # run asynchronously
#$ActionResumeRetryCount -1 # infinite retries if host is down
# remote host is: name/ip:port, e.g. 192.168.0.1:514, port optional
#*.* @@remote-host:514
# TCP/SSL Test
# $ModLoad imuxsock # local messages
$ModLoad imtcp # TCP listener
# $PrivDropToGroup rsyslog
# $PrivDropToUser rsyslog
# make gtls driver the default
$DefaultNetstreamDriver gtls
# certificate files
# $DefaultNetstreamDriverCAFile /opt/pem/ca.pem
# $DefaultNetstreamDriverCertFile /opt/pem/machine-cert.pem
# $DefaultNetstreamDriverKeyFile /opt/pem/machine-key.pem
$DefaultNetstreamDriverCAFile /home/rsyslog/tls/myCert.pem
$DefaultNetstreamDriverCertFile /home/rsyslog/tls/myCert.pem
$DefaultNetstreamDriverKeyFile /home/rsyslog/tls/myKey.key
$InputTCPServerStreamDriverAuthMode anon
$InputTCPServerStreamDriverMode 1 # run driver in TLS-only mode
$InputTCPServerRun 514 # start up listener at port 1514
# 保存syslog file path
# $template Remote,"/var/log/syslog/%fromhost-ip%/%$YEAR%-%$MONTH%-%$DAY%.log"
# $template ipRemote,"/var/log/syslog/%FROMHOST-IP%/%$YEAR%-%$MONTH%-%$DAY%.log"
# if $fromhost-ip == '10.10.0.100' then ?ipRemote
# & ~
$template Remote,"/home/rsyslog/%fromhost-ip%/%$YEAR%-%$MONTH%-%$DAY%.log"
:fromhost-ip, !isequal, "127.0.0.1" ?Remote
& ~
# ### end of the forwarding rule ###证书保存情况:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9[rsyslog@linux-syslogserver ~]$ pwd
/home/rsyslog
[rsyslog@linux-syslogserver ~]$ ll
total 16
drwx------. 2 rsyslog rsyslog 28 May 4 06:27 10.10.0.100
-rw-rw-r--. 1 rsyslog rsyslog 4 May 4 06:58 log.pid
-rw-------. 1 rsyslog rsyslog 262 May 4 06:55 nohup.out
-rw-r--r--. 1 rsyslog rsyslog 4498 May 4 06:57 rsyslog.conf
drwx------. 2 rsyslog rsyslog 41 May 4 05:54 tls
2.3 指定/usr/sbin/rsyslogd能使用1024以下端口
指定/usr/sbin/rsyslogd程序能使用1024以下端口
~ ] setcap cap_net_bind_service=+eip /usr/sbin/rsyslogd
补充:取消程序使用1024以下端口(不要执行)
~ ] setcap -r /path/to/application
2.4 修改/var目录下的log文件权限
让rsyslog用户有写的权限。
1 | |
2.5 修改/var/lib/rsyslog目录权限
这一步很重要含义:让rsyslog用户能读取imjournal.state文件。
2
3
4
5
6
7[root@rsyslog-server rsyslog]# chmod -R 722 /var/lib/rsyslog
# 原权限为:
[root@rsyslog-server rsyslog]# ll /var/lib
drwx------. 2 root root 29 Mar 8 04:11 rsyslog
# 更改后权限为:
[root@rsyslog-server rsyslog]# ll /var/lib
drwx-w--w-. 2 root root 29 Mar 8 04:11 rsyslog
2.6 使用命令行启动rsyslogd程序
1 | |
2.7 配置检查
1 | |